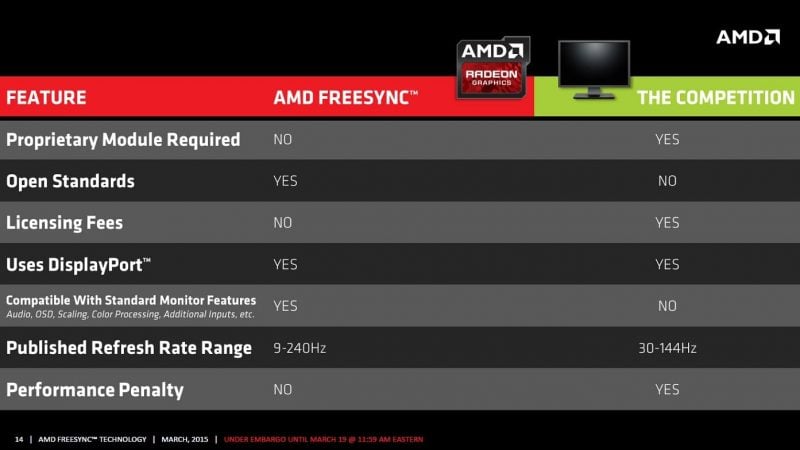
AMD FreeSync, or Project FreeSync, is AMD’s dynamic refresh rate technology designed to help eliminate screen tearing, eliminate studdering, and for mobile devices, improve battery life. AMD FreeSync is the direct competitor to Nvidia’s G-Sync adaptive refresh rate technology.
Why Dynamic Refresh Rate is Important
Dynamic or adaptive refresh rate technology is important because video content is not always sent to the display at the display’s native refresh rate. Take for example a game. During times when little is happening in the scene, framerates could easily hit 150 FPS or higher while during scenes of high activity such as an intense firefight, frames could dip down to 30FPS or lower.
As monitors have traditionally only only operated at a fixed 60Hz (60 FPS) or newer monitors at 144Hz (144 FPS), during scenes where little is happening the user will experience screen tearing, while during scenes where a lot is happening the user will experience studdering or lag.
AMD FreeSync Versions
FreeSync
The original implementation of AMD FreeSync, which we’ll refer to as FreeSync 1, includes all the basic features of FreeSync.
FreeSync 2
In January during CES 2017, AMD announced FreeSync 2 which added HDR 10-bit display support, automatic mode switching, and LFC (Low Framerate Compensation).
AMD FreeSync vs Nvidia G-Sync
AMD FreeSync was first released back in 2015 shortly after Nvidia announced G-Sync. Unlike Nvidia’s G-Sync solution which was expensive to license and implement, AMD promised FreeSync to be a similar variable refresh rate technology that would not only be free of charge, but would also be adopted by VESA, the Video Electronics Standards Association, as a part of their DisplayPort 1.2a specification under Adaptive Sync. As a result, any monitor that’s DisplayPort 1.2a compliant will support AMD Freesync.
How Do I Use AMD Freesync?
In order to use AMD FreeSync, you’ll need to purchase a FreeSync compatible monitor, and a FreeSync compatible AMD graphics card or AMD APU. FreeSync compatible graphics cards include the AMD Radeon R7 and newer and FreeSync compatible APUs include the AMD A6-7400K and newer.
AMD FreeSync Monitor Database
| Monitor | Size | Resolution | Type | Min Refresh Rate | Max Refresh Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acer XR342CK | 34-inch | 3440×1440 | IPS | 48 Hz | 75 Hz |
| AOC Agon AG271QX | 27-inch | 2560×1440 | TN | 40 Hz | 144 Hz |
| AOC G2460PF | 24-inch | 1920×1080 | TN | 35 Hz | 144 Hz |
| AOC G2460PQU | 24-inch | 1920×1080 | TN | 50 Hz | 146 Hz |
| AOC G2460VQ6 | 24-inch | 1920×1080 | TN | 48 Hz | 75 Hz |
| BenQ EX3200R | 31.5-inch | 1920×1080 | VA | 45 Hz | 144 Hz |
| BenQ XL2730 | 27-inch | 2560×1440 | TN | 40 Hz | 144 Hz |
| LG 24MP59G-P | 24-inch | 1920×1080 | IPS | 56 Hz | 75 Hz |
| LG 29UM68-P | 29-inch | 2560×1080 | IPS | 56 Hz | 75 Hz |
| Nixeus NX-EDG27 | 27-inch | 2560×1440 | AHVA | 30 Hz | 144 Hz |
| Nixeus NX-VUE24 | 24-inch | 1920×1080 | TN | 30 Hz | 144 Hz |
| ViewSonic XG2701 | 27-inch | 1920×1080 | TN | 30 Hz | 144 Hz |